MySql - Port 3306
Become VeryLazyTech member! 🎁
Follow us on:
✖ Twitter @VeryLazyTech.
👾 Github @VeryLazyTech.
📜 Medium @VeryLazyTech.
📺 YouTube @VeryLazyTech.
📩 Telegram @VeryLazyTech.
🕵️♂️ My Site @VeryLazyTech.
Visit our shop for e-books and courses. 📚
Basic info
MySQL can be described as an open source Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) that is available at no cost. It operates on the Structured Query Language (SQL), enabling the management and manipulation of databases.
Default port: 3306
How to connect?
For local:
mysql -u root # Connect to root without password
mysql -u root -p # A password will be asked (check someone)For remote
Enumeration
Some of the enumeration actions require valid credentials
Write any binary data
Once you've used CONVERT(unhex(...), BINARY) or CONVERT(from_base64(...), BINARY) to generate binary data in MySQL, you can leverage it to write files directly to the filesystem using INTO DUMPFILE. This is especially powerful when you have FILE privileges in MySQL. For example, to drop a simple PHP web shell, you could run:
That writes a PHP shell accessible at http://target/shell.php?cmd=id.
You can also write binary payloads (e.g., .so or .dll) like this:
Or write a malicious cron job:
These commands let you pivot from database access to full system compromise, persistence, or remote code execution, all without a traditional shell.
MySQL commands
MySQL Permissions Enumeration
Credential Discovery
If you didn’t get lucky with anonymous login, time to brute.
🧾 Default Credentials
Common ones to try:
root:rootroot:tooradmin:admin
💣 Brute Force with Hydra
⚔️ Medusa Alternative
Reading Arbitrary Files via MySQL Client Misuse
One lesser-known but powerful technique involves abusing the LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE feature in MySQL/MariaDB. This command, when used with the LOCAL keyword, instructs the client (not the server) to read a local file and send it to the database server.
If an attacker can trick a victim's MySQL client (like the mysql CLI or an app with misconfigured DB connections) into connecting to a malicious server, that rogue server can request the client to read and send any local file — leading to arbitrary file disclosure.
🔍 Vulnerable Command Example
Note the keyword LOCAL — this is what triggers the client-side file read. If LOCAL is omitted, and MySQL is hardened, you may see this error:
This behavior can be exploited by running a rogue MySQL server and luring clients into connecting to it (e.g., through phishing, SSRF, or misconfigured dev tools). You can find a working proof of concept here: 👉 Rogue MySQL Server PoC
Further reading:
Full attack walkthrough: Seebug.org Whitepaper
Simplified overview: RussianSecurity Expert
Privilege Escalation in MySQL
🔎 Check MySQL Service User
It’s especially dangerous if MySQL is running as root, as that can lead to full system compromise. Check who runs MySQL:
⚙️ Dangerous MySQL Configs to Look For
In /etc/mysql/my.cnf or mysqld.cnf, pay attention to:
user: Account running MySQL (should NOT be root)secure_file_priv: If unset, file import/export is unrestrictedadmin_address: Exposed MySQL interfacesdebug,sql_warnings: Might expose sensitive info in logs
🔐 Extracting User Credentials and Privileges
👤 Create a New Privileged User
💻 Get a Local Shell via MySQL
Useful in cases where your client has interactive capabilities.
🧬 Privilege Escalation via Malicious Shared Library (UDF Injection)
If MySQL is running as root or a privileged user, you can execute OS commands by injecting a User Defined Function (UDF) from a compiled .so or .dll.
📦 Compile UDF Library on Target (Linux)
🧪 Inject Library via SQL
🪟 Windows Variant
🔑 Extracting MySQL Passwords from the Filesystem
If you have file system access, here are some critical files to check:
📂 /etc/mysql/debian.cnf
/etc/mysql/debian.cnfContains plain-text login credentials for debian-sys-maint:
💾 /var/lib/mysql/mysql/user.MYD
/var/lib/mysql/mysql/user.MYDHolds raw MySQL user hashes — extract like this:
This can give you credentials even without database access.
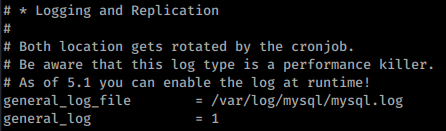
Enabling logging
You can enable logging of mysql queries inside /etc/mysql/my.cnf uncommenting the following lines:
Useful files
Configuration Files
windows *
config.ini
my.ini
windows\my.ini
winnt\my.ini
<InstDir>/mysql/data/
unix
my.cnf
/etc/my.cnf
/etc/mysql/my.cnf
/var/lib/mysql/my.cnf
~/.my.cnf
/etc/my.cnf
Command History
~/.mysql.history
Log Files
connections.log
update.log
common.log
Default MySQL Databases and Tables
When MySQL or MariaDB is freshly installed, it comes with a set of default databases and system tables that play critical roles in authentication, configuration, and user management. The most important of these is the mysql database, which stores core internal data used by the MySQL server. Inside it, you'll find sensitive tables like:
mysql.user– Stores usernames, password hashes, and global privilegesmysql.db– Defines database-level privilegesmysql.tables_priv,columns_priv– Fine-grained access control over specific tables or columnsmysql.procs_priv– Procedure-specific privilegesmysql.roles_mapping– Role-based access configuration (in newer versions)
These tables are often the first target during post-exploitation. By querying or dumping them, an attacker can extract valid user accounts, escalate privileges, or even inject backdoor users. For example:
Accessing these default tables is essential for both privilege auditing and credential extraction, and manipulating them can allow the attacker to create new admin accounts, escalate permissions, or disable security controls. Always monitor access to the mysql database and restrict usage to only highly trusted administrators.
ALL_PLUGINS
APPLICABLE_ROLES
CHARACTER_SETS
CHECK_CONSTRAINTS
COLLATIONS
COLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITY
COLUMNS
COLUMN_PRIVILEGES
ENABLED_ROLES
ENGINES
EVENTS
FILES
GLOBAL_STATUS
GLOBAL_VARIABLES
KEY_COLUMN_USAGE
KEY_CACHES
OPTIMIZER_TRACE
PARAMETERS
PARTITIONS
PLUGINS
PROCESSLIST
PROFILING
REFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTS
ROUTINES
SCHEMATA
SCHEMA_PRIVILEGES
SESSION_STATUS
SESSION_VARIABLES
STATISTICS
SYSTEM_VARIABLES
TABLES
TABLESPACES
TABLE_CONSTRAINTS
TABLE_PRIVILEGES
TRIGGERS
USER_PRIVILEGES
VIEWS
INNODB_LOCKS
INNODB_TRX
INNODB_SYS_DATAFILES
INNODB_FT_CONFIG
INNODB_SYS_VIRTUAL
INNODB_CMP
INNODB_FT_BEING_DELETED
INNODB_CMP_RESET
INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX
INNODB_CMPMEM_RESET
INNODB_FT_DELETED
INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE_LRU
INNODB_LOCK_WAITS
INNODB_TEMP_TABLE_INFO
INNODB_SYS_INDEXES
INNODB_SYS_TABLES
INNODB_SYS_FIELDS
INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX_RESET
INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE
INNODB_FT_DEFAULT_STOPWORD
INNODB_FT_INDEX_TABLE
INNODB_FT_INDEX_CACHE
INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES
INNODB_METRICS
INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN_COLS
INNODB_CMPMEM
INNODB_BUFFER_POOL_STATS
INNODB_SYS_COLUMNS
INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN
INNODB_SYS_TABLESTATS
GEOMETRY_COLUMNS
SPATIAL_REF_SYS
CLIENT_STATISTICS
INDEX_STATISTICS
USER_STATISTICS
INNODB_MUTEXES
TABLE_STATISTICS
INNODB_TABLESPACES_ENCRYPTION
user_variables
INNODB_TABLESPACES_SCRUBBING
INNODB_SYS_SEMAPHORE_WAITS
columns_priv
column_stats
db
engine_cost
event
func
general_log
gtid_executed
gtid_slave_pos
help_category
help_keyword
help_relation
help_topic
host
index_stats
innodb_index_stats
innodb_table_stats
ndb_binlog_index
plugin
proc
procs_priv
proxies_priv
roles_mapping
server_cost
servers
slave_master_info
slave_relay_log_info
slave_worker_info
slow_log
tables_priv
table_stats
time_zone
time_zone_leap_second
time_zone_name
time_zone_transition
time_zone_transition_type
transaction_registry
user
accounts
cond_instances
events_stages_current
events_stages_history
events_stages_history_long
events_stages_summary_by_account_by_event_name
events_stages_summary_by_host_by_event_name
events_stages_summary_by_thread_by_event_name
events_stages_summary_by_user_by_event_name
events_stages_summary_global_by_event_name
events_statements_current
events_statements_history
events_statements_history_long
events_statements_summary_by_account_by_event_name
events_statements_summary_by_digest
events_statements_summary_by_host_by_event_name
events_statements_summary_by_program
events_statements_summary_by_thread_by_event_name
events_statements_summary_by_user_by_event_name
events_statements_summary_global_by_event_name
events_transactions_current
events_transactions_history
events_transactions_history_long
events_transactions_summary_by_account_by_event_name
events_transactions_summary_by_host_by_event_name
events_transactions_summary_by_thread_by_event_name
events_transactions_summary_by_user_by_event_name
events_transactions_summary_global_by_event_name
events_waits_current
events_waits_history
events_waits_history_long
events_waits_summary_by_account_by_event_name
events_waits_summary_by_host_by_event_name
events_waits_summary_by_instance
events_waits_summary_by_thread_by_event_name
events_waits_summary_by_user_by_event_name
events_waits_summary_global_by_event_name
file_instances
file_summary_by_event_name
file_summary_by_instance
global_status
global_variables
host_cache
hosts
memory_summary_by_account_by_event_name
memory_summary_by_host_by_event_name
memory_summary_by_thread_by_event_name
memory_summary_by_user_by_event_name
memory_summary_global_by_event_name
metadata_locks
mutex_instances
objects_summary_global_by_type
performance_timers
prepared_statements_instances
replication_applier_configuration
replication_applier_status
replication_applier_status_by_coordinator
replication_applier_status_by_worker
replication_connection_configuration
replication_connection_status
replication_group_member_stats
replication_group_members
rwlock_instances
session_account_connect_attrs
session_connect_attrs
session_status
session_variables
setup_actors
setup_consumers
setup_instruments
setup_objects
setup_timers
socket_instances
socket_summary_by_event_name
socket_summary_by_instance
status_by_account
status_by_host
status_by_thread
status_by_user
table_handles
table_io_waits_summary_by_index_usage
table_io_waits_summary_by_table
table_lock_waits_summary_by_table
threads
user_variables_by_thread
users
variables_by_thread
host_summary
host_summary_by_file_io
host_summary_by_file_io_type
host_summary_by_stages
host_summary_by_statement_latency
host_summary_by_statement_type
innodb_buffer_stats_by_schema
innodb_buffer_stats_by_table
innodb_lock_waits
io_by_thread_by_latency
io_global_by_file_by_bytes
io_global_by_file_by_latency
io_global_by_wait_by_bytes
io_global_by_wait_by_latency
latest_file_io
memory_by_host_by_current_bytes
memory_by_thread_by_current_bytes
memory_by_user_by_current_bytes
memory_global_by_current_bytes
memory_global_total
metrics
processlist
ps_check_lost_instrumentation
schema_auto_increment_columns
schema_index_statistics
schema_object_overview
schema_redundant_indexes
schema_table_lock_waits
schema_table_statistics
schema_table_statistics_with_buffer
schema_tables_with_full_table_scans
schema_unused_indexes
session
session_ssl_status
statement_analysis
statements_with_errors_or_warnings
statements_with_full_table_scans
statements_with_runtimes_in_95th_percentile
statements_with_sorting
statements_with_temp_tables
sys_config
user_summary
user_summary_by_file_io
user_summary_by_file_io_type
user_summary_by_stages
user_summary_by_statement_latency
user_summary_by_statement_type
version
wait_classes_global_by_avg_latency
wait_classes_global_by_latency
waits_by_host_by_latency
waits_by_user_by_latency
waits_global_by_latency
x$host_summary
x$host_summary_by_file_io
x$host_summary_by_file_io_type
x$host_summary_by_stages
x$host_summary_by_statement_latency
x$host_summary_by_statement_type
x$innodb_buffer_stats_by_schema
x$innodb_buffer_stats_by_table
x$innodb_lock_waits
x$io_by_thread_by_latency
x$io_global_by_file_by_bytes
x$io_global_by_file_by_latency
x$io_global_by_wait_by_bytes
x$io_global_by_wait_by_latency
x$latest_file_io
x$memory_by_host_by_current_bytes
x$memory_by_thread_by_current_bytes
x$memory_by_user_by_current_bytes
x$memory_global_by_current_bytes
x$memory_global_total
x$processlist
x$ps_digest_95th_percentile_by_avg_us
x$ps_digest_avg_latency_distribution
x$ps_schema_table_statistics_io
x$schema_flattened_keys
x$schema_index_statistics
x$schema_table_lock_waits
x$schema_table_statistics
x$schema_table_statistics_with_buffer
x$schema_tables_with_full_table_scans
x$session
x$statement_analysis
x$statements_with_errors_or_warnings
x$statements_with_full_table_scans
x$statements_with_runtimes_in_95th_percentile
x$statements_with_sorting
x$statements_with_temp_tables
x$user_summary
x$user_summary_by_file_io
x$user_summary_by_file_io_type
x$user_summary_by_stages
x$user_summary_by_statement_latency
x$user_summary_by_statement_type
x$wait_classes_global_by_avg_latency
x$wait_classes_global_by_latency
x$waits_by_host_by_latency
x$waits_by_user_by_latency
x$waits_global_by_latency
Learn & practice For the Bug Bounty
Support VeryLazyTech 🎉
Become VeryLazyTech member! 🎁
Follow us on:
✖ Twitter @VeryLazyTech.
👾 Github @VeryLazyTech.
📜 Medium @VeryLazyTech.
📺 YouTube @VeryLazyTech.
📩 Telegram @VeryLazyTech.
🕵️♂️ My Site @VeryLazyTech.
Visit our shop for e-books and courses. 📚
Last updated