Brute Force - Services, web, local, tools & wordlists
A comprehensive brute force guide covering web logins, APIs, and local services like IMAP, MySQL, and LDAP using tools like Hydra, Medusa, Legba, and more.
Default Credentials
📚 Top Resources for Default Credentials:
Create Your Own Dictionaries
Crunch – Custom Pattern Generator
Website-Based Wordlists
CUPP (Common User Passwords Profiler)
Wister – Wordlist Mutator
Pydictor – Advanced Dictionary Generator

Tools
Hashcat
Hashcat modes
Common Services
AMQP (ActiveMQ, RabbitMQ, Qpid, etc.)
Cassandra / ScyllaDB
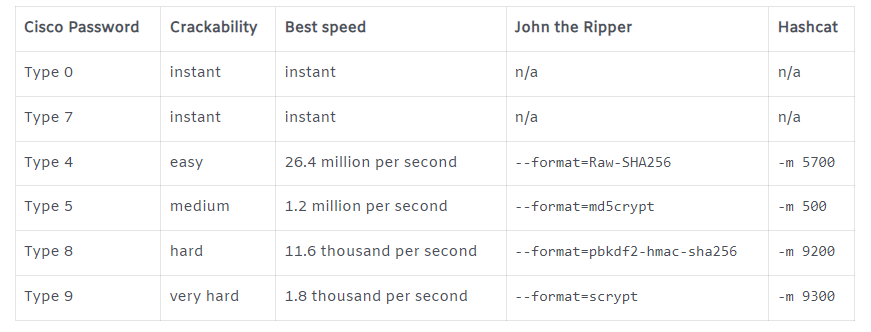
Cisco
CouchDB
Elasticsearch
HTTP Burte Force
Login Form bruteforce
Bruteforce Directory/RESTful bruteforce
Arjun parameters wordlist
Path Parameters BF
Header Authentication
Cookie/Header bruteforce (vhost brute)
Host
HTTP Verbs (methods) bruteforce
Using file
Using inline list
Directory & Files Bruteforce
HTTP Basic Auth
HTTP - NTLM
HTTP - Post Form
HTTP - CMS -- (W)ordpress, (J)oomla or (D)rupal or (M)oodle
Keberoasting
Keepass
Lucks image
NTLM cracking
Open Office Pwd Protected Column
PDF
PDF Owner Password
PGP/GPG Private key
PostgreSQL
PFX Certificates
RDP
Redis
SFTP
SQL Server
Weak SSH keys / Debian predictable PRNG
STOMP (ActiveMQ, RabbitMQ, HornetQ and OpenMQ)
VNC
Winrm
ZIP
Known plaintext zip attack
7z
Online cracking databases
Last updated